Supplementation with Conserved M2 Ectodomains and Neuraminidase VLPs Enhances Cross Protective Efficacy of Influenza Vaccines
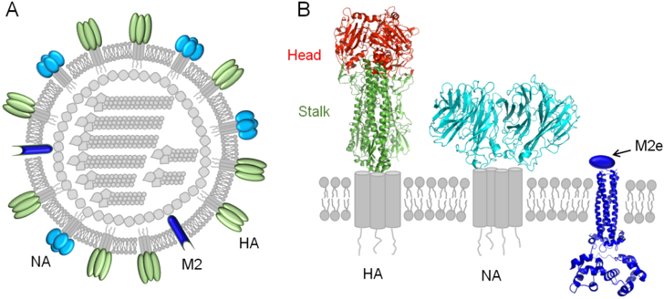
Due to constant changes and mutations in the influenza virus, a new vaccine is needed almost every season to combat the emerging strains. The purpose of this research is to target two conserved elements of the influenza virus, the M2 ectodomain (M2e) and neuraminidase (NA), in order to achieve cross-protection when on its own or combined with a current influenza split vaccine. In this study, we investigated the effects of a bivalent H1N1 and H3N2 split vaccine supplemented with a multi-neuraminidase virus-like particles (m-cNA-M2e VLP) vaccine, consisting of M2e tandem repeat M2e5x, consensus N1 NA, consensus N2 NA, and consensus Flu B NA, on inducing immunogenicity and cross-protection in young and aged female BALB/c mice. Groups of mice were intramuscularly immunized with split vaccine alone, m-cNA-M2e VLP vaccine alone, or split plus m-cNA-M2e VLP vaccines twice (prime-boost) at a 3-week-interval, and then challenged with a homologous (H1N1), heterologous (H3N2) or heterosubtypic (rgH5N1) influenza virus strain. All groups of vaccinated and challenged (infected) mice were compared with naïve infection (non-vaccinated infected) mice. The split plus m-cNA-M2e VLP-immunized mice effectively induced higher levels of virus-specific immunoglobulin (Ig)G antibodies after boost vaccination and lower body weight loss after challenge with heterologous H3N2 virus or heterosubtypic rgH5N1 virus, indicating better cross-protection than the other comparing groups. These findings suggest that the supplementation of influenza split vaccine with m-cNA-M2e VLP vaccine is effective in providing improved cross-protection and may be utilized alongside current influenza vaccines to confer broader protection against newly emerging influenza virus strains.
 CLOSE SIDEBAR
CLOSE SIDEBAR